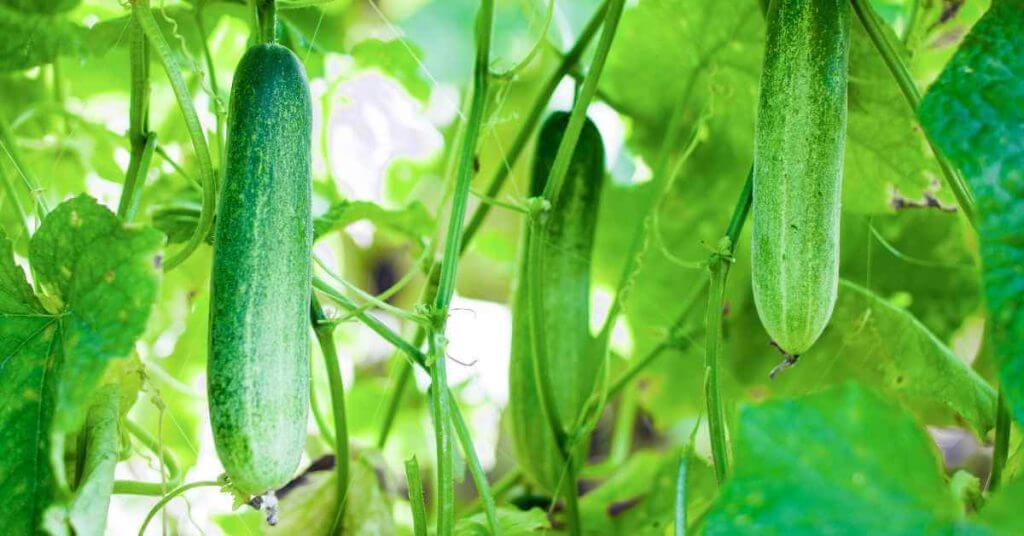

The 5 Best Companion Plants For Cucumbers
Here is a list of the 5 best companion plants for cucumbers that will help your cucumbers, and your garden as a whole, thrive.

Many, myself included, first became interested in gardening through the desire to grow more of their own food and reduce dependence on expensive and often pesticide-ridden fruit and vegetables from questionable sources.
Naturally, I focused on fruits and vegetables to try and maximize my yield by planting my crops as tightly as possible, neglecting companion plants such as flowers and herbs.
This was one of my many (many) mistakes on my journey to successfully growing my own vegetables, and I soon learned that flowers are an essential component to any garden for increasing plant health and maximizing yield.
That’s why this article will focus on the importance of adding flowers as companions for your fruits, vegetables, and herbs, and how they can improve your crop health as well as increase your yield.
While many dismiss companion planting as a myth (admittedly, a lot of information about companion planting is hearsay and not well evidenced), polyculture – growing multiple crop species together in the same area – is an age-old agricultural process that has been shown to enhance biodiversity, improve soil health, and increase crop yields.
Flowers act as beneficial companion plants through five key mechanisms:
A combination of flowers such as geraniums, marigolds, and nasturtiums tick almost all of these boxes, adding multiple benefits while taking very little – flowers are typically small and do not require lots of water nutrients that might otherwise compete with your more valuable crops.
Year after year, marigolds and geraniums remain essential flowers in my plots. Their small size ensures they do not take up valuable growing space, while their pest-deterring and pollinating abilities will increase the health and fruit set of your prized vegetables and fruits.
As an added benefit, vibrant flowers add a splash of much-needed color to otherwise monotonous green and brown vegetable plots.
I also try to incorporate borage, with its beautiful blue star-shaped leaves and nasturtiums into the mix, two plants that benefit through pollination, pest repellent, weed suppression, sheltering, and soil health.
Borage is not the best option for small plots, however; it tends to grow thick and wide and will take up valuable crop space if space is an issue for you.
You can truly use whichever flowers appeal the most to you; there are very few flowers that do not provide some sort of benefit, except for the larger ones consuming space and blocking sunlight for smaller plots.

When it comes to flowers, you only really have to watch out for two issues.
The first is space. Larger flowers like borage need to be managed to ensure they do not grow so large that they block sunlight and take up valuable space.
Secondly, planting them too close to deep-rooted and heavy-feeding vegetables such as tomatoes, potatoes, and carrots can harm flowers that also require larger amounts of water and nutrients, particularly geraniums, lupins, and sunflowers. Consider planting such flowers away from deep-rooted vegetables (at least 24 inches) to ensure they do not compete with one another.

The table below shows which flowers are best for helping other plants and which provide the best companions. As you can see, flowers are givers and tend to provide great benefits for others. The only flowers on the avoid list are those that require moderate amounts of water and nutrients and tend to compete with other plants when planted too close.
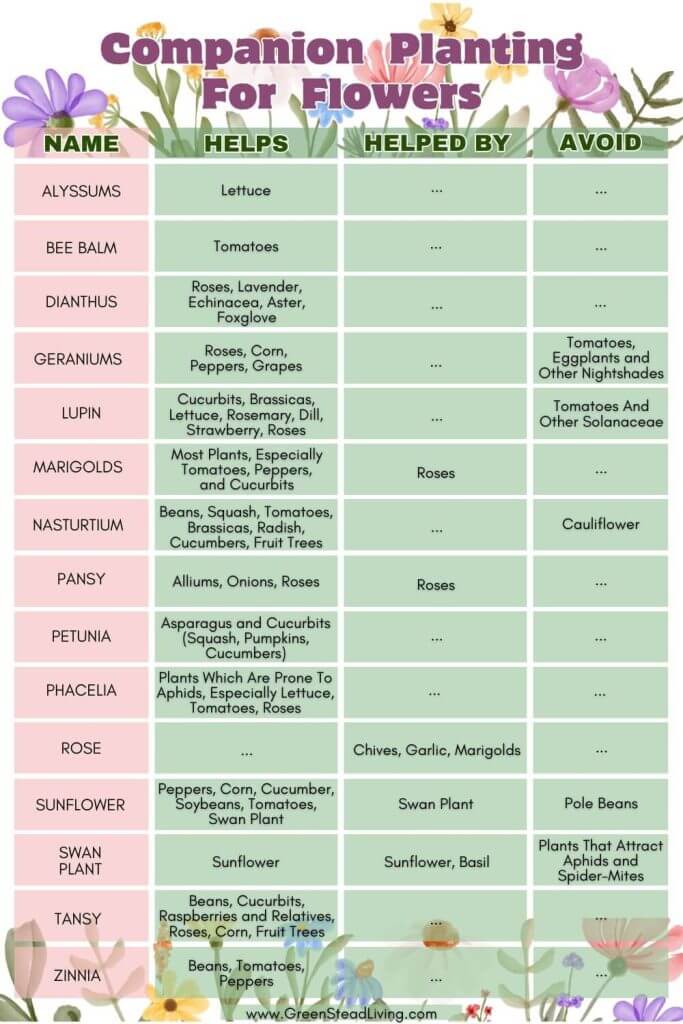
Adding flowers to your vegetable garden does more than just pretty things up – they provide a range of benefits that help your other crops grow healthier and stronger.
Flowers like marigolds, geraniums, and nasturtiums are hard workers—improving soil, warding off pests, and helping with pollination. Incorporating these plants isn’t just a visual upgrade; it’s a smart gardening tactic that makes your vegetable plot healthier and more productive.
Whether you’re a beginner or have been gardening for years, remember that these flowers do a lot more than just look good—they’re essential helpers that keep your garden thriving.
Flowers act as beneficial companion plants through five key mechanisms:
Year after year, marigolds and geraniums remain essential flowers in my plots. Their small size ensures they do not take up valuable growing space, while their pest-deterring and pollinating abilities will increase the health and fruit set of your prized vegetables and fruits.
As an added benefit, vibrant flowers add a splash of much-needed color to otherwise monotonous green and brown vegetable plots.
When it comes to flowers, you only really have to watch out for two issues.
The first is space. Larger flowers like borage need to be managed to ensure they do not grow so large that they block sunlight and take up valuable space.
Secondly, planting them too close to deep-rooted and heavy-feeding vegetables such as tomatoes, potatoes, and carrots can harm flowers that also require larger amounts of water and nutrients, particularly geraniums, lupins, and sunflowers. Consider planting such flowers away from deep-rooted vegetables (at least 24 inches) to ensure they do not compete with one another.

Here is a list of the 5 best companion plants for cucumbers that will help your cucumbers, and your garden as a whole, thrive.

An easy beginners guide on how to make compost, the right way, for a healthier garden.

An overview of everything you need to know about what is companion planting, and what plants should be included and avoided to help your garden thrive.

A companion planting chart for fruits, showing which plants help fruits, which are helped by fruit plants, and which to avoid.

A guide to Silkie chickens and everything you need to know about the breed before you buy.

Here is a comprehensive and easy to follow companion planting chart for vegetables, based on available scientific literature and trial and error experience.